A Brief History of Domestic Cats
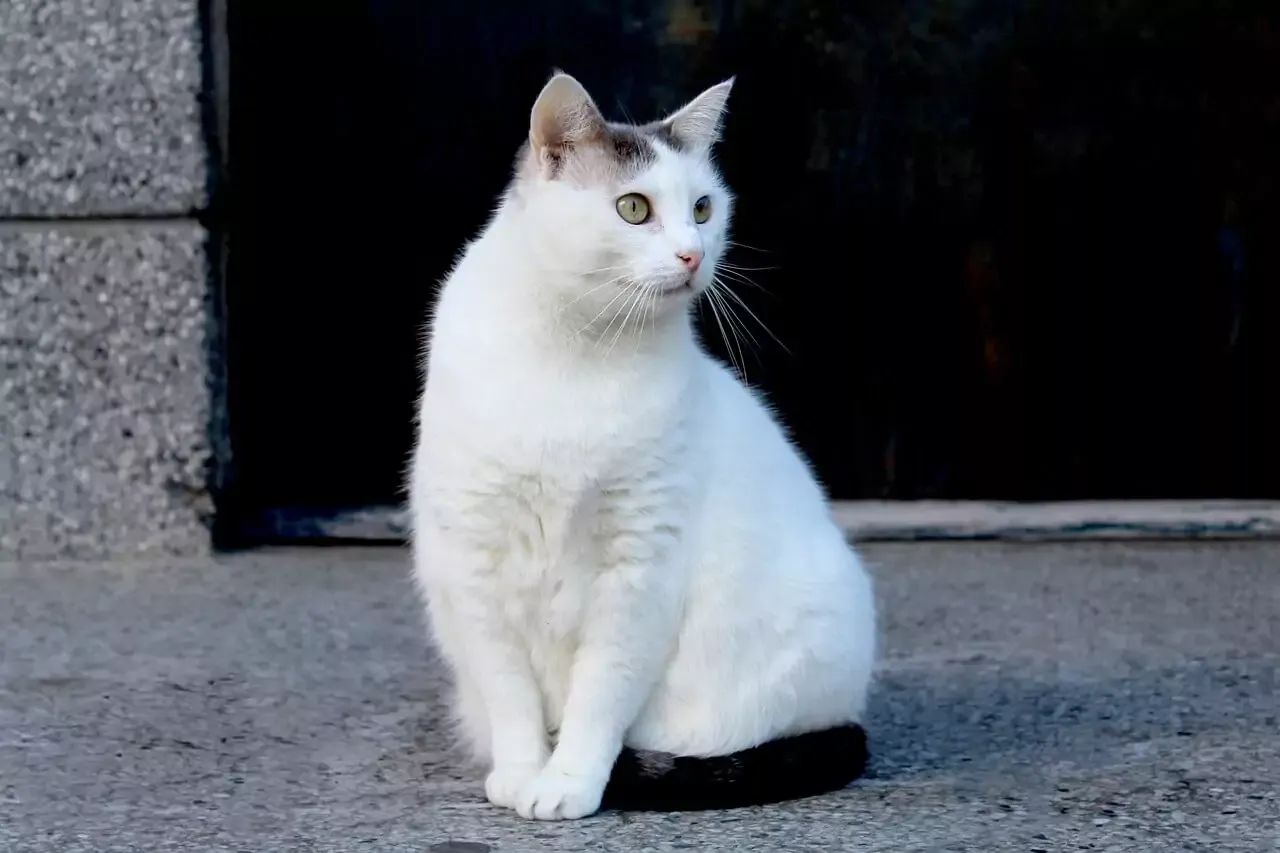
Domestic cats are one of the most popular pets in the world. Everyone likes them for their calm nature and attitude. They have adapted themselves to the environment all over the world. Domestic Cats are the second most popular pet in the world.
 |
| Domestic Cats |
Who are the domestic cats:
There are 36 live cat species in the world. Domestic cats are one of the species among them. The domestic cat is Carnivore mammals. They are a member of the Felidae family, which belongs to the Cordata phylum.
Are domestic cats one species or breed?
The domestic cat is not a breed, it's one of the specific species that comes from the cat's family. According to ICZN (International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature), the domestic cat is a distinct species. The scientific name of the domestic cat is Felis catus.
In the year 1758, Carl Linnaeus has proposed the scientific name Felis catus for a domestic cat. Also, More than three names were proposed by other scientists. In the year 2003, ICZN only ruled that the Domestic cat scientific name is Felis catus.
History of Domestic Cats:
The history of domestic cats is Too old. In this article, We will describe the history of domestic cats with three points.
The Ancestor of the domestic cats.
When we discuss the history of the domestic cat, then there has a question who is the ancestor of domestic cats?
Scientists have different opinions about the ancestor of Domestic cats. Most scientists believe that domestic cats are the successors of the Middle East wildcat Felis silvestris lybica. This concept is based on the analysis of DNA and skeletal size of wild cats in The Middle East.
In a study in 2007, scientists collected approximately 1,000 wild cats' DNA from different parts of the world. They compared it with the DNA of domestic cats. This shows that the DNA of the Middle East wild cats (Felis silvestris lybica) is be related to the DNA of purebred domestic cats.
In 2004, a 9500-year-old cat skeleton was found in a cemetery that was buried with a human. After analysis of this Archaeological evidence ( teeth and bone ), scientists find a close relation between Middle East wild cats with domestic cats.
After analysis of DNA, Skeleton and Behavioral characteristic scientist conclude that the Middle East wild cats (Felis silvestris lybica) are the ancestor of Domestic cats.
The Origin of domestic cats:
Many believe that cats were first domesticated in the Middle East about 12,000 years ago. Although in China about 15,000 years ago, pottery was shown with wonderful cat pictures that resembled ordinary cats in the present. Scientists are still trying to find out the Origin of cats.
In the year 1983, a cat's jawbone was found during an archaeological excavation in Cyprus. The jawbone is estimated to be 8,000 years old. The researchers guessed that since no wild cats had a chance to visit the island, also there were no native mammals on the island. So the idea is that it will be the jawbone of any domestic cat. Which may have come to the island by ship with people. Based on this, it was thought that cats first began to be domesticated 8,000 years ago.
In 2004, a 9500-year-old cat skeleton was found that's evidence of cat domestication 9500 years ago.
Another study was conducted in 2017 at the University of Leuven to find out the history of domestic cats. They collected and analyzed 200 cats' DNA found at different times in archaeological sites in Africa and Europe. It shows that cats range in age from a least 100 to most of 12,000 years.
History Of Domestication:
Domestication is so much longer process. It's not like kept a wild cat in a cage and has become domesticated. Researcher Eva Maria Giegel says cats start to domesticate in two steps. First in a country in the eastern and later in Egypt.
When domesticated, cats did not move directly into human homes. They have lived in an open environment around people for a long time after domesticated. This may be thousands of years. The wild cats have undergone some genetic changes for this long time. Although the wild cats did not change much when they were domesticated.
Scientists speculate that The abundance of food has brought cats from the wild to the human environment. There were a lot of rats on the farmer's farm. The rats ate the crops of the field. Wild cats came from the wild to the human environment to hunt these rats. Wild cats hunted rats to meet their own food needs, while farmers' crops were protected from rats. People are taking wild cats as their friends for this beneficial role. This mutually beneficial role of humans and wild cats has made cats the primary means of domestication.
From 2465-2150 BC, cats were considered sacred animals because cats benefited the farmer by hunter rats. That's the time people think a cat was a supernaturally powerful animal because of its ability to catch rats. So people used to worship cats in temples. Although at that time, no one cared for a cat as a pet animal.
Wildcats adapt easily to the environment around humans. As a result, the wild nature between them has decreased from generation to generation. They adapted themself to people. At the same time the cat's social behavior, size, body language, love of play, high intelligence has inspired human. As a result, the ancient Egyptian people started worshiped to cats and since then, the cats were domesticated in the house.
There is another opinion that, Nearly 9,000 years ago, in the Neolithic Age, the farmers of the East were able to domesticate the wild cats for the first time for killing rats.
Anyway, A few hundred years later, these wild pet cats spread beyond Egypt, across the seabed, to the wider part of the Middle East, and the Atlantic coast.
How did the cats spread all over the world?
Before and after domestication the relationships between humans with cats had a beneficial role. In the past, people used to keep cats in their homes to protect stored food from rats. At the same time, food was stored on ships for export to different countries. Cats were also sheltered on ships to protect that food from rats. In this way, cats have spread all over the world by ship. Cats spread throughout Europe in the Roman period.
Currently, Domestic cats are seen everywhere except the continent of Antarctica.
Modern Domestic Cats:
During domestication, cats have undergone only minor changes in anatomy and behavior, and that they are still capable of surviving in the wild. Egypt and African wildcats contributed to the maternal gene pool of the domestic cat at a later time.
Several natural behaviors and characteristics of wildcats may have preadapted them for domestication as pets. After a long time, these cats were isolated from the wild cat as a separated species name domestic cat.
DNA analysis has shown that the DNA of modern domestic cats is almost similar to Felis silvestris lybica. That's proving that modern domesticated cat species come from The middle east wild cat Felis silvestris lybica.
Felis silvestris lybica still survive in the wild. They are solitary nocturnal predators. Which can be seen among domesticated tabby cats.
Usually, different species of members of the same family do not perform reproductive functions in the natural environment. But the domestic cats and the wild cats Are different species of the same family, Interbreeding can be seen between them. So genetic diversity is found between wild cats and domestic cats. As a result, the number of purebred wild cats and domestic cats is declining.
01. American Bobtail Cat Breed full Profile | A Unique Analysis
02. Balinese cat breed-History, Personality, Health, Care andFacts