Bull Elk Rut Behavior | Bull Elk Bugling in Rut Season
 |
| Bull Elk in Rut |
The elk rut, also known as the elk breeding season, is a fascinating and integral part of the natural cycle in North America. It is a period when male elk, known as bulls, become highly active and vocal as they compete for attention and mating rights with female elk.
During the elk's rut, several events occur in phases. In this post, we will discuss the elk rut behavior step by step.
Bull Elk Rut Behavior Step by Step
Elk Rut Timing:
The elk rut typically takes place in the early fall, although the exact timing can vary based on geographic location and environmental conditions. In many regions, it begins in September and continues into early October.
Bull Elk Behavior:
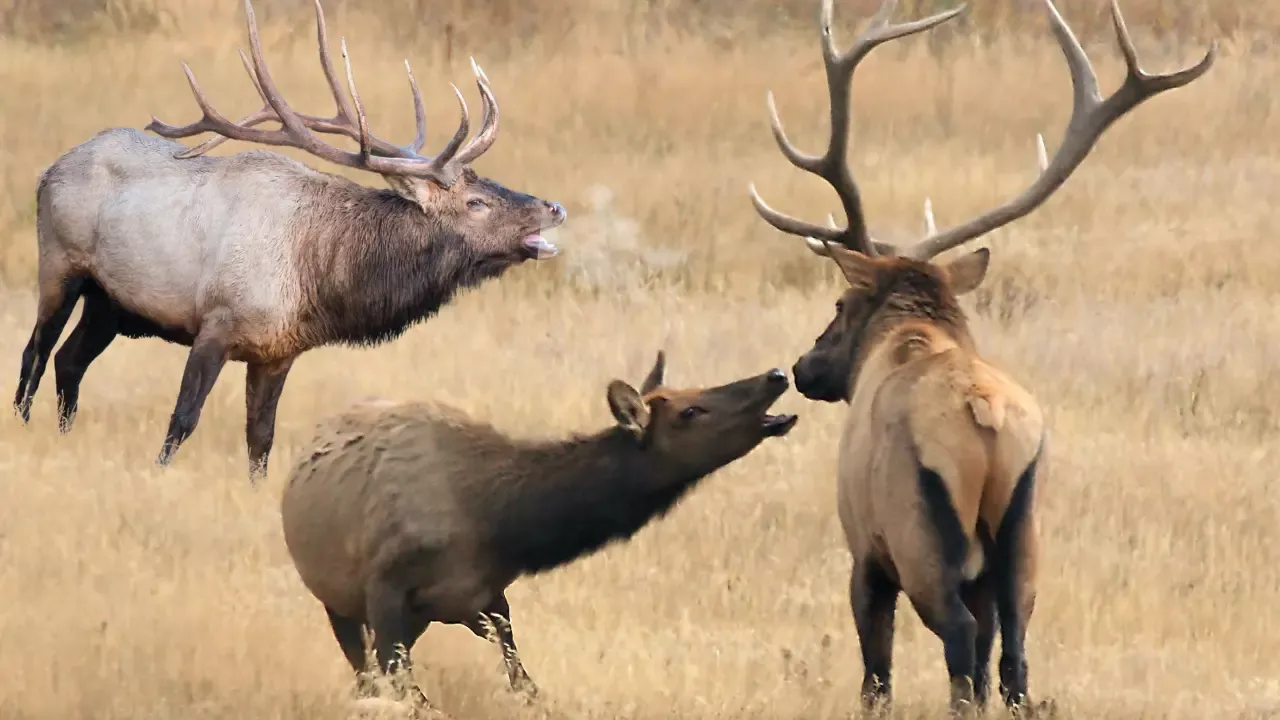
The dominant feature of the elk rut is the striking transformation of bull elk during this time. Bulls grow massive antlers over the summer, and these antlers are used as weapons to establish dominance and compete for mates. The larger and more impressive the antlers, the more likely a bull is to attract females.
Bugling:
One of the most iconic aspects of the elk rut is the bugling sound produced by bull elk. Bugling is a haunting and eerie call that can be heard echoing through the mountains and forests. Bulls use bugles to assert their dominance, communicate with other males, and attract potential mates. These calls can be heard for miles and serve as a way for bulls to challenge each other's authority.
Fighting for Dominance:
Bulls engage in physical combat to establish their dominance and access to the females. These battles can be intense and often result in loud clashes of antlers. The victor typically earns the right to mate with a group of receptive females. The stronger and larger bulls generally have the advantage, but younger and smaller bulls may also compete for a chance to mate.
Gathering Females:
Dominant bulls collect a group of females into a harem. Females are typically in estrus for a short period, so the bull must keep them close to maximize their chances of mating. They closely guard these cows to prevent other bulls from mating with them. This protective behavior is intense, as the competition among bulls for access to the females is fierce.
Courtship Rituals:
Female elk come into estrus during the rut. This is the period when they are fertile and receptive to mating. The courtship rituals of the elk rut are both fascinating and intricate. Bulls display various behaviors to entice females, such as rolling in dirt, wallowing in mud, and even urine spraying to create a strong, musky scent. These actions are designed to make the bull more appealing to the females.
Grazing and Rest:
The rut is a physically demanding time for both bulls and cows. Bulls often lose a significant amount of body weight due to the energy expended in bugling, fighting, and herding females. Once the rut is over, they need to replenish their energy by grazing and resting.
Natural Selection:
The intense competition among bulls during the rut is a mechanism of natural selection. The strongest, healthiest, and most dominant bulls are more likely to pass on their genes to the next generation. This results in a strong and resilient elk population over time.
Reproduction:
After a successful courtship, mating takes place. The gestation period for female elk is about 8.5 months, so calves are typically born in late spring or early summer, allowing them to take advantage of the lush vegetation and milder weather.