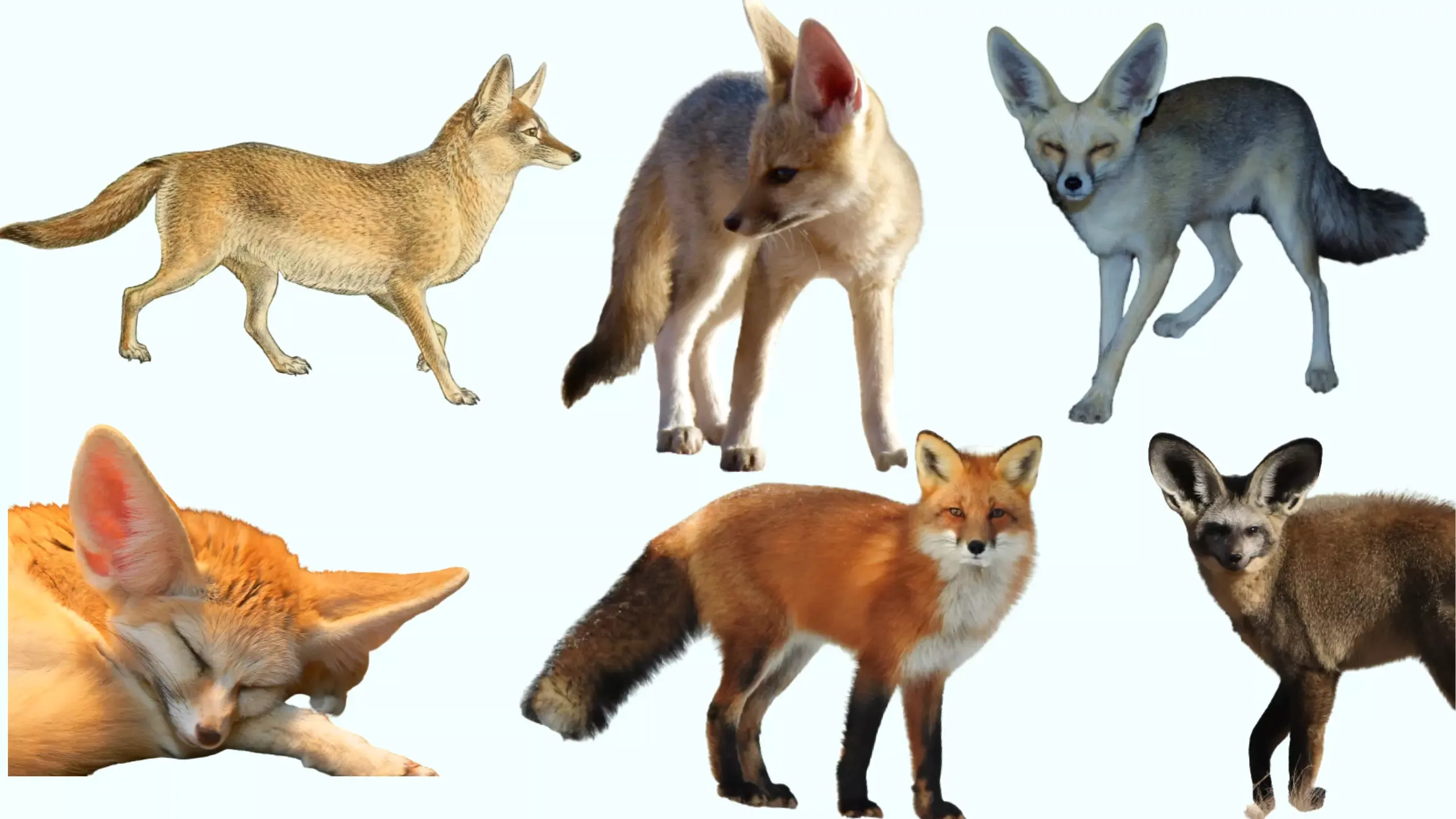
Foxes in Africa | African Foxes Range, Habitat, Diet and Lifespan
African wildlife is a diverse and captivating tapestry of nature's marvels. This continent is a sanctuary for incredible biodiversity. Vast savannas, dense jungles, and arid deserts host a plethora of species. Africa is home to nearly a million species of animals, from the heaviest elephant on land to the tallest giraffe, the strongest lion, and the fastest cheetah. Among the millions of species of animals, there are some species of foxes found across the continent of Africa. In today's post, we will introduce you to the types of fox species that are found across the African continent.
 |
| Foxes in Africa |
Types of Foxes in Africa
Africa's vast savannas, dense jungles, and arid deserts are sanctuaries for wildlife. The animals of this region are specially adapted to thrive in the arid environment. Commonly, five species of foxes are found across the African continent but many believe that red foxes are also found in some areas of African Northern Fringes. As such, six species of foxes are found throughout Africa. These are-
01. Fennec Fox
02. Bat-eared Fox,
03. Cape Fox,
04. Rüppell's Fox
05. Pale Fox
06. Red Fox
Let's learn more about these six species of Foxes in Africa.
01. The Fennec Fox
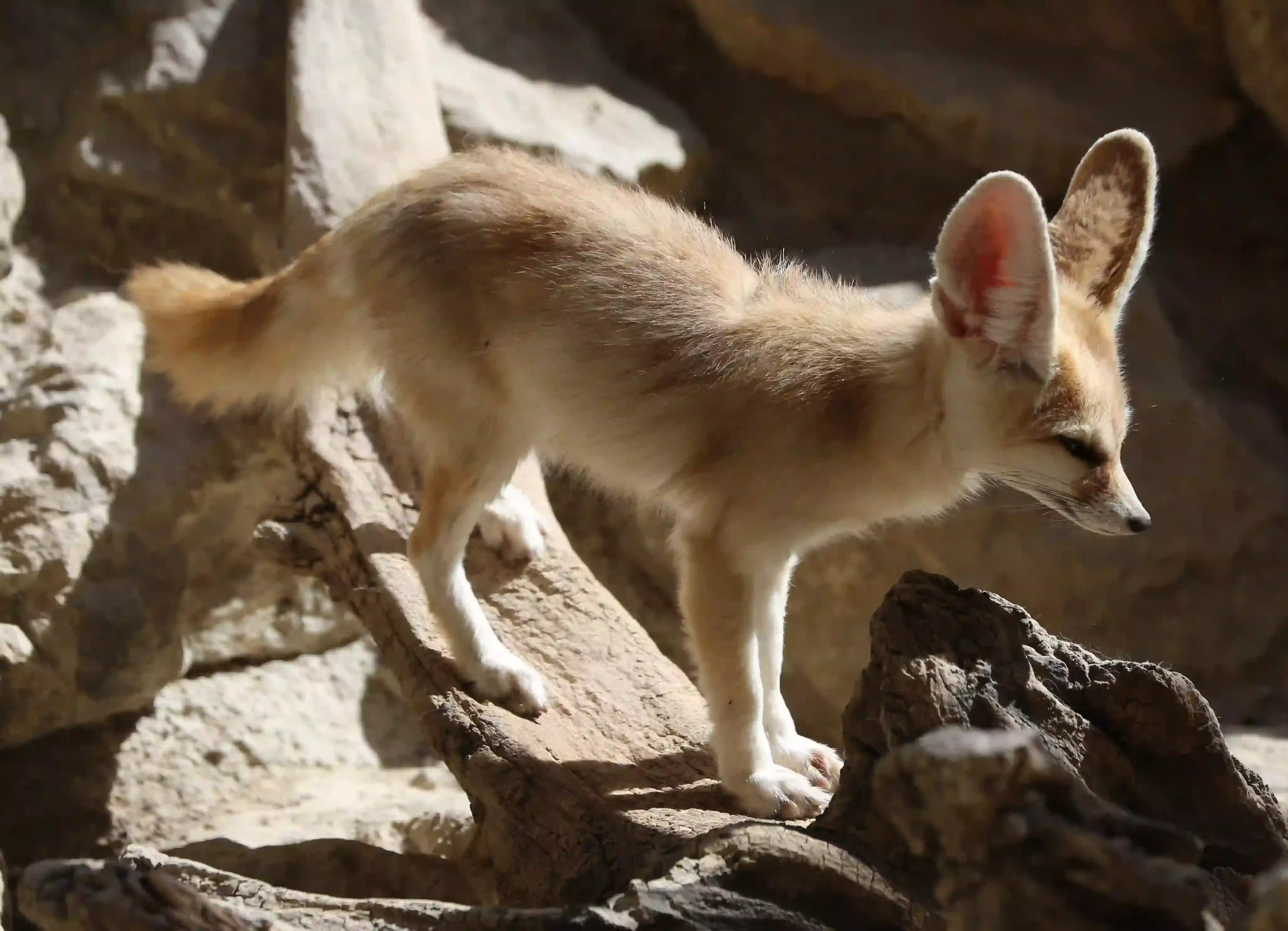 |
| Fennec Fox |
Common Name: Fennec Fox
Scientific Name: Vulpes zerda
Distribution and Habitat:
The fennec fox is primarily found in the desert regions of North Africa. Its range includes countries such as Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Mauritania, Mali, Niger, Chad, Sudan, Tunisia, and Morocco. Within these countries, the Fennec Fox inhabits the Sahara Desert and other arid regions, where it has adapted to the harsh desert environment. It prefers sandy areas and avoids the more vegetated regions, as it is specially adapted to the desert's extreme conditions, using its large ears to dissipate heat and locate prey underground.
Diet:
Fennec foxes are omnivorous mammals. Their diet includes insects (grasshoppers and locusts), small rodents, lizards, birds, eggs, fruits, and occasionally roots and leaves.
Lifespan:
Their average lifespan in the wild is 10 years, and in captivity, it is 14 years.
Conservation Status:
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Fennec foxes are listed as Least Concern.
This diminutive fox, measuring about 9–16 inches in length, boasts distinctively large ears, perfect for dissipating heat in its arid habitat. The fennec fox is perfectly adapted to its environment. Its nocturnal nature allows it to avoid extreme daytime temperatures, while its keen senses aid in hunting. Their remarkable adaptations to the desert environment make them one of the most intriguing and adorable creatures in the wild.
02. The Bat-eared Fox
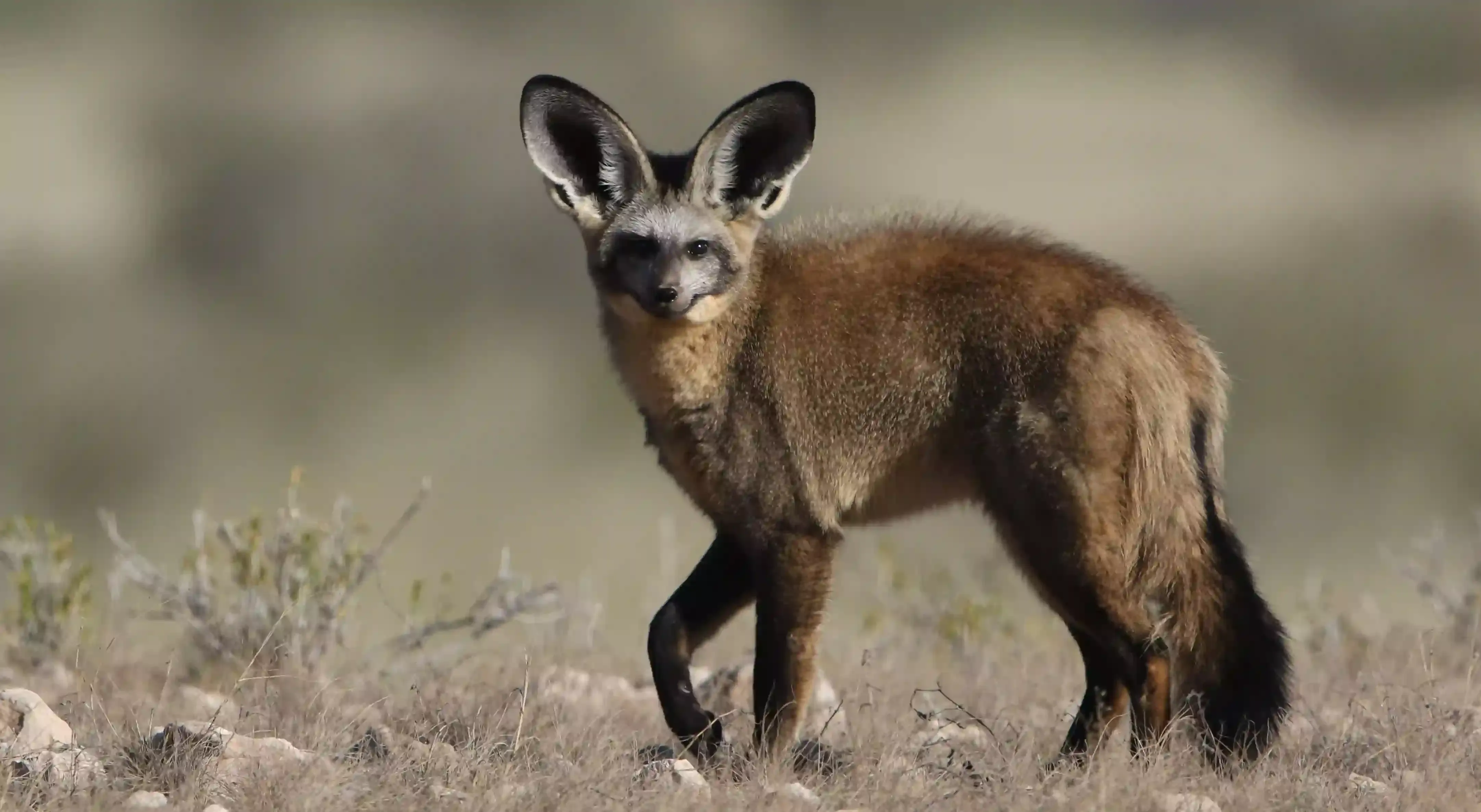 |
| Bat-eared Fox |
Common Name: Bat-eared Fox
Scientific Name: Otocyon megalotis
Distribution and Habitat:
The bat-eared Fox is primarily found in the grasslands and savannas of Africa. Its distribution includes South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Angola, Zambia, Malawi, Mozambique, Tanzania, Kenya, Somalia, and Ethiopia.
The Bat-eared Fox prefers open, flat areas with short grass and sparse vegetation, as these habitats provide a rich food source. This fox species typically avoids dense forests and desert regions, and its range is generally limited to the grassy and savanna areas of sub-Saharan Africa.
Diet:
Fennec foxes are insectivores. Their 80% diet source is insects, especially termites and dung beetles. They also eat all kinds of insects, arthropods, small rodents, small lizards, birds, and eggs.
Lifespan:
Bat-eared foxes have a long lifespan. Their average lifespan in the wild is 13 years, and in captivity it is 17 years.
Conservation Status:
According the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) the Bat-eared foxes are listed as Least Concern.
The Bat-eared fox is recognizable by its enormous ears; it measures about 13–16 inches in length and weighs around 4–7 pounds. Their sandy coat blends well with their open habitat, and their unique ears aid in hunting. They are highly social animals, living in family groups and communicating through various vocalizations.
03. The Cape Fox
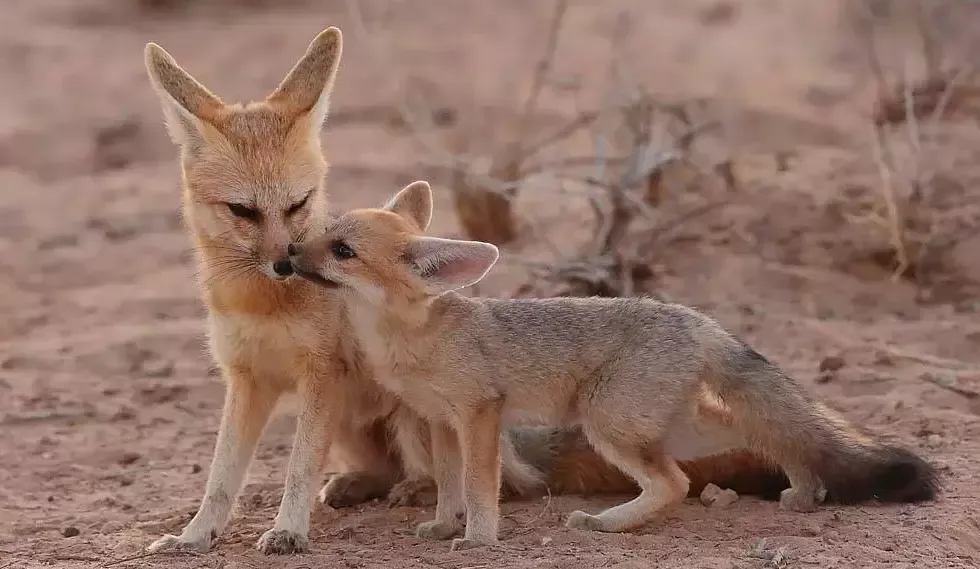 |
| Cape Fox |
Common Name: Cape Fox, Cama Fox, or Silver-backed Fox
Scientific Name: Vulpes chama
Distribution and Habitat:
The Cape Fox is native to southern Africa. It is found in several countries across the region, including South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Angola, Zambia, and Mozambique. The Cape Fox primarily inhabits arid and semi-arid regions, such as grasslands, savannas, and scrublands. It is well adapted to these environments.
Diet:
The Cape Fox is omnivorous and feeds on a variety of food sources, including small mammals, birds, fruits, insects, and even carrion.
Lifespan:
Their average lifespan in the wild is 10 years, and in captivity, it is 14 years.
Conservation Status:
According the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) the Bat-eared foxes are listed as Least Concern.
The Cape Fox's name comes from its natural habitat in the Cape region. With a silver-gray coat and black-tipped tail, it exhibits remarkable adaptability to various habitats. Cape Foxes are primarily nocturnal, using their acute senses to hunt under the cover of darkness.
04. The Rüppell's Fox
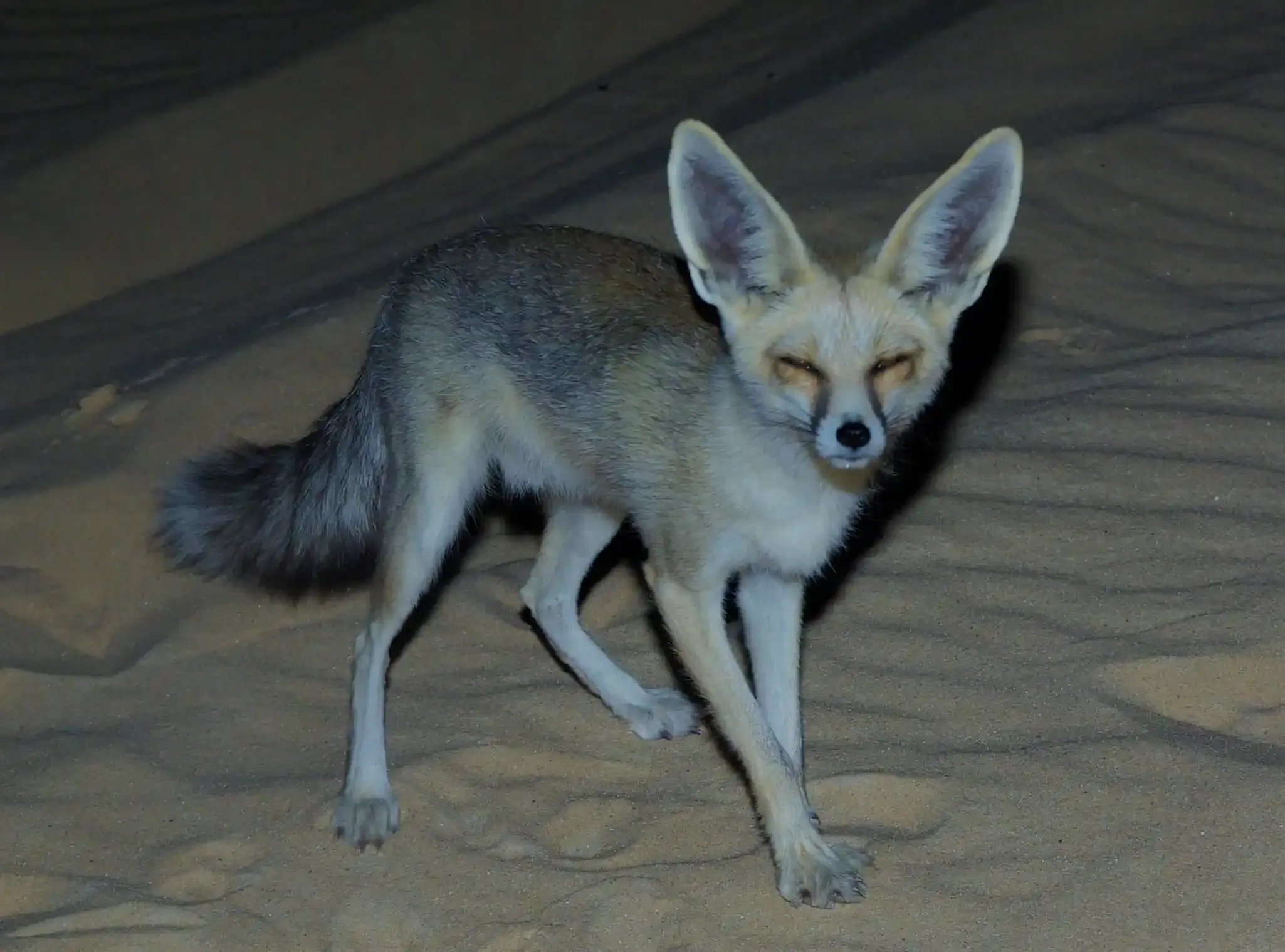 |
| Rüppell's Fox |
Common Name: Rüppell's Fox or Rüppell's sand fox
Scientific Name: Vulpes rueppelli
Distribution and Habitat:
Rüppell's fox is native to North Africa and parts of the Middle East. Its range includes several countries in these regions, including Egypt, Libya, Sudan, Chad, Niger, Mauritania, Mali, Algeria, Tunisia, Morocco, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Israel, and Yemen. Rüppell's Fox is well-adapted to arid and desert environments, and it inhabits sandy and stony deserts, semi-deserts, and scrublands.
Diet:
Rüppell's foxes are omnivorous mammals. It primarily feeds on a variety of prey, including small mammals, insects, birds, and fruits.
Lifespan:
Their average lifespan in the wild is 7 years, and in captivity it is 12 years.
Conservation Status:
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Rüppell's Fox is listed as Least Concern.
Rüppell's Fox is a small fox named after the German naturalist and explorer Eduard Rüppell. Rüppell's Fox has distinctively large ears and a sandy or pale yellowish-gray coat that provides excellent camouflage in its habitat. Rüppell's Fox is well-adapted to life in the desert and semi-desert regions. Ruppell's foxes are nocturnal and solitary animals. Their keen sense of hearing and exceptional digging skills help them locate food and create burrows for shelter.
05. The Pale Fox
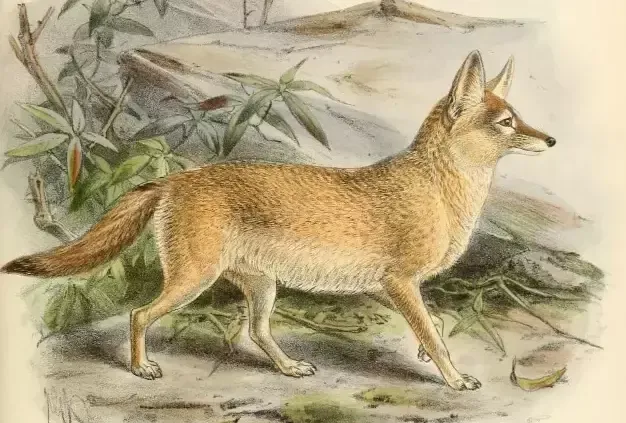 |
| Pale Fox |
Common Name: Pale Fox or Pallid Fox
Scientific Name: Vulpes pallida
Distribution and Habitat:
The Pale Fox is found in the Sahel region of Africa. The range of the Pale Fox includes countries are Senegal, Mauritania, Mali, Niger, Chad, Sudan, South Sudan, Burkina Faso and Nigeria.
The Pale Fox inhabits a range of habitats, including savannas, grasslands, and semi-arid regions. It is well-adapted to its arid environment.
Diet:
Pale foxes are omnivorous mammals. Primarily, it feeds on small mammals, birds, insects, and fruits.
Lifespan:
Their average lifespan in the wild is 10 years, and in captivity, it is 16 years.
Conservation Status:
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Pale Fox is listed as Least Concern.
The Pale Fox is named for its light-colored, pale coat, which provides effective camouflage in its sandy and rocky desert habitat. The Pale Fox is well-adapted to survive in the hot and dry conditions of the Sahel, which includes savannas, grasslands, and semi-deserts. It is primarily a nocturnal and solitary hunter. Due to its remote and elusive nature, much of its behavior and population status remain relatively understudied.
06. The Red Fox
 |
| Red Fox |
Common Name: Red Fox
Scientific Name: Vulpes vulpes
Distribution and Habitat:
The Red Fox is a widely distributed and adaptable fox species. Its range covers a diverse array of countries across North America, Europe, Asia, and the African Northern Fringes. The red fox has a broad distribution across many regions within its native range. The fox's ability to thrive in various habitats, including forests, grasslands, mountains, and urban areas, has contributed to its widespread presence in different countries.
Diet:
Red Fox are omnivorous and opportunistic hunters, preying on small mammals, birds, insects, and even scavenging on carrion.
Lifespan:
Their average lifespan in the wild is 3–4 years, and in captivity, it is 17 years.
Conservation Status:
According the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Red Fox are listed as Least Concern.
The Red Fox is known for its beautiful reddish-brown fur, although variations in color can occur, ranging from silver to almost black. With its cunning nature and remarkable ability to thrive in diverse environments, the red fox has become an iconic and fascinating member of the animal kingdom.
Conclusion:
Due to habitat destruction, deforestation, agriculture and industrialization, natural disasters, climate change, the number of this fox species in the wild environment is constantly decreasing. We must all strive to protect these African foxes in the wild.